Table of Contents
DNA: Deoxyribonucleic Acid

The full form of DNA is “Deoxyribonucleic Acid“. Deoxy means lack of oxygen atom, Ribo means ribose sugar. Nuclei are found in the nucleus of the cell. Acid contains negatively charged phosphate ion which is acidic. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is a molecule that encodes an organism’s genetic blueprint. In other words, DNA contains all of the information required to build and maintain an organism.
What is DNA?
DNA is the hereditary material for humans and most other living beings. That is, they carry genetic information for the growth, development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms. DNA is present in the nucleus of every cell in the body and the genetic instructions are stored in the form of a code composed of 4 nitrogenous bases: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G) and Thymine (T)
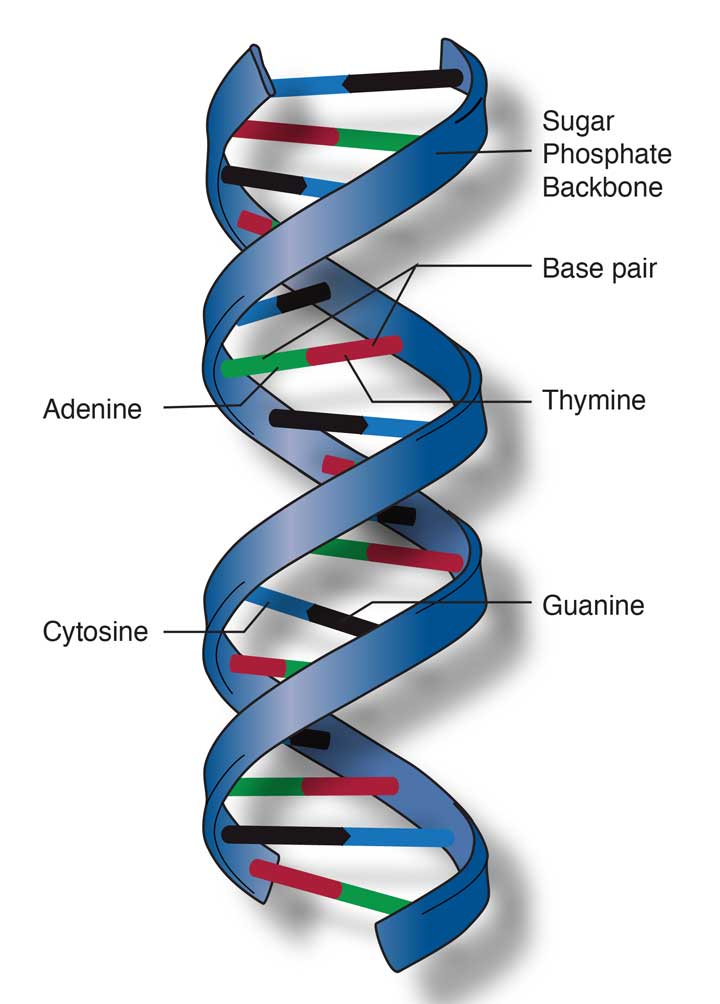
- Adenine, ‘A,’ It has a 2-ring structure, making it a purine.
- Thymine, ‘T,’ is a pyrimidine, which means it has a 1-ring structure.
- Guanine, the ‘G,’ part of both DNA and RNA, where it binds to cytosine Binds with.
- Cytosine, ‘C,’ is part of DNA and RNA and binds with Guanine. It has a ring, so it is a pyrimidine.
Functions of DNA
DNA is the genetic material which carries all the hereditary information. Genes are the small segments of DNA, consisting mostly of 250 – 2 million base pairs. Apart from storing genetic information, DNA is involved in:
- Replication: DNA makes carbon copies through replication. This allows DNA to transfer genetically from old cells to new cells (from one generation to the next).
- Transcription: Here the information on the DNA is written down onto a different molecule called the RNA. This molecule acts as a messenger to carry the information to other parts of the cell.
- Genetic Information: It transmits genetic information from one generation to another.
- Cellular Metabolism: It regulates the metabolic reactions of cells with the help of enzymes, hormones and specific RNAs.
- Evolution: It controls the development of organisms through the internal genetic clock.
- DNA Finger Printing: Each person has their own DNA sequence that is not in common with others. This property of DNA is used in DNA finger printing, a technique used to identify a person by his or her DNA.
Other full forms of DNA
| Full Form | Category |
|---|---|
| Daily News and Analysis | News |
| Direcţia Naţională Anticorupţie [National Anti-corruption Division] | Departments & Agencies |
| Democratic National Assembly | Politics |
| Does Not Apply | Military |
| Genentech, Incorporated | NYSE Symbols |
| Do Not Accept | General Business |
| Data Not Available | Databases |
| Do Not Assume | Chat |
| Did Not Attend | Oncology |
| Do Not Ask | Chat |
| Defense Nuclear Agency | Military |
| Do Not Answer | Telecom |
| Distributed interNet Applications | General Computing |
| Digital Network Architecture | General Computing |
| Do Not Adjust | Electronics |
| Digital Nonlinear Accelerator | General Computing |
| National Dyslexic Association | Non-Profit Organizations |
| Douglas Noel Adams, writer and dramatist | Famous & Celebs |
| Dynamic Network Analysis | Networking |
| Distributed Network Application | Software |
| Distributed Net Applications | Networking |
| Don't Need Advice | Chat |
| Digital Network Alert | Networking |
| Department Network Administrator | Occupation & Positions |
| Divine Nature and Attributes | Religion |
| Daytime, Night-time, Anytime | Telecom |